Understanding Integrated Wastewater Treatment Systems
Wastewater treatment is a critical process in maintaining water quality and protecting both human health and the environment. An integrated wastewater treatment system is a sophisticated approach that combines various technologies and processes to efficiently treat water before it is released back into the environment or reused. In this comprehensive article, we will explore how these systems work, the benefits they offer, their components, and the challenges and solutions associated with their implementation.
Introduction to Integrated Wastewater Treatment Systems
An Integrated Wastewater Treatment System (IWTS) is a coordinated combination of physical, chemical, and biological processes designed to remove contaminants from wastewater. The concept of integration in wastewater treatment involves optimizing different treatment methods to create a more effective and efficient overall system. This holistic approach aims to meet strict discharge regulations, reduce environmental impact, and potentially recover resources such erry water, nutrients, or even energy.
What Wastewater Contains
Before delving into the specifics of IWTS, it’s essential to understand what we’re treating. Wastewater typically contains:
- Suspended solids
- Organic pollutants
- Nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus
- Pathogens
- Heavy metals
- Emerging contaminants, such as pharmaceuticals and personal care products
Objectives of Integrated Wastewater Treatment
The main objectives of integrated wastewater treatment are:
- To improve the quality of wastewater to meet effluent standards
- To minimize the ecological footprint of treatment operations
- To reduce operational costs and increase treatment efficiency
- To achieve water reuse objectives and recover valuable resources
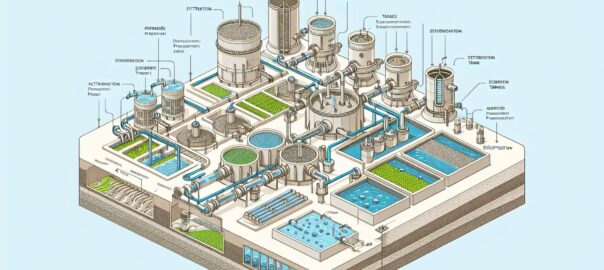
Components of an Integrated Wastewater Treatment System
An IWTS may include several components, such as:
- Preliminary Treatment: Screens, grit chambers, and pre-sedimentation tanks that remove large solids and grit.
- Primary Treatment: Settling tanks or clarifiers that allow suspended solids to settle.
- Secondary Treatment: Biological processes like activated sludge systems, biofilters, or constructed wetlands that break down organic matter.
- Tertiary Treatment: Advanced treatment processes such as microfiltration, ultrafiltration, reverse osmosis, and UV disinfection that further remove solids, nutrients, and pathogens.
- Sludge Treatment: Processes that treat and stabilize the solids removed from the wastewater.
- Advanced Control Systems: Such as SCADA and real-time monitoring sensors that manage the treatment processes, ensuring optimal performance.
Benefits of Integrated Wastewater Treatment
The benefits of integrating these components into a single treatment system include:
- Enhanced Efficiency: Integrated systems optimize the performance of each treatment stage, resulting in higher-quality effluent.
- Cost Savings: Efficiency gains can translate to lower operational expenses.
- Flexibility: IWTS can be customized to treat various types of wastewater and fluctuating loads.
- Resource Recovery: Integrated systems can facilitate the recovery of water, energy, and nutrients.
- Reduced Footprint: An IWTS can often achieve the same or better treatment levels in a smaller footprint than traditional systems.
- Compliance: Advanced control and monitoring help to ensure regulatory compliance.
Challenges of Integrated Wastewater Treatment Systems
Implementing an IWTS comes with its challenges:
- High Capital Costs: The initial investment for these systems can be significant.
- Complexity: Integrated systems are complex and require skilled personnel for operation and maintenance.
- Technology Integration: Combining various technologies into a seamless system can be challenging.
- Regulatory Approval: Meeting regulations for water reuse and discharge can be a lengthy and complicated process.
Solutions to Overcome the Challenges
Despite the challenges, there are solutions in place to address these concerns:
- Phased Implementation: Gradual installation and commissioning can spread out costs and allow time for staff training.
- Qualified Personnel: Investing in education and training ensures the workforce can competently manage IWTS.
- Technology Partnerships: Working with experienced technology providers can ease integration complexities.
- Research and Development: Continuous improvement of IWTS technology can bring down costs and simplify regulatory compliance.
Case Studies and Examples
There are numerous examples of successful IWTS implementations globally. For instance, the Orange County Water District (OCWD) in California employs an integrated system for water reuse [1]. Another example is the NEWater project in Singapore, which uses advanced integrated treatment processes to reclaim wastewater [2].
Future of Integrated Wastewater Treatment Systems
The future of IWTS is promising, with trends indicating:
- Increased digitization: Utilizing the Internet of Things (IoT) for better system management and data-driven decision-making.
- Sustainable practices: Greater focus on resource recovery and energy neutrality.
- Customization: More tailored systems to meet specific needs of different regions and industries.
Conclusion
Integrated Wasterwater Treatment Systems represent a holistic and sophisticated approach to wastewater management. The integration of advanced technologies and processes offers a multitude of benefits, including improved efficiency, compliance with regulations, and potential resource recovery. While challenges in cost, complexity, and technology persist, innovative solutions and a focus on training and development continue to drive the IWTS field forward.
Sources
- Orange County Water District – Integrated water reuse solutions: https://www.ocwd.com/
- NEWater Singapore – Pioneering water reuse practices: https://www.pub.gov.sg/watersupply/fournationaltaps/newater
- Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) – Wastewater treatment principles and regulations: https://www.epa.gov/wastewater-management
By approaching wastewater treatment from an integrated perspective, communities and industries are not only addressing pressing environmental concerns but also paving the way for sustainable water management practices that could lead to water security and resilience in the face of growing demand and changing global climates.